In the wake of COVID-19, warehouses look to implement scalable processes to manage unpredictable demand. Emerging technologies are focused on refining the warehouse operations through the utilization of advanced systems such as warehouse scanning systems and barcode warehouse management systems, with a particular emphasis on efficiently managing inventories.
Traditional inventory management is slow, messy, and prone to errors. QR code inventory management is fast, accurate, and easy. QR code inventory management is the best solution for businesses that need to track their physical products efficiently.
In the 1990s, Denso Wave Corporation innovated QR codes to encode additional information on product labels. These labels, integrated into a warehouse barcode system and utilized through barcode scanners for warehouse inventory, play a pivotal role in streamlining complex warehouse operations and expanding consumer outreach. This method serves as an effective means to store relevant product information in-store, especially for individuals who are used to spreadsheet-based solutions.
WHAT IS A QR CODE?
QR codes (short for “Quick Response”) are two-dimensional barcodes in a a warehouse management system. You can scan them in both directions i.e vertically and horizontally. Instead of a single linear sequence of black lines and white spaces, you’ll get small square codes that convey a lot of information about product details
The QR code’s pixelated pattern strengthens its ability to store information. A single QR code stores more than 4,000 characters. The code can include product information as well as links to images, videos, and dedicated websites. Through the utilization of WMS scanners and a warehouse barcode scanning system, both employees and customers can effortlessly access crucial information about the specific part or product they are examining.
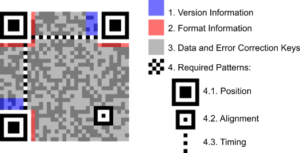
QR codes offer enhanced versatility and capabilities compared to traditional one-dimensional barcodes. They can store a wealth of product information, including product details, batch numbers, serial numbers, and other relevant data. This makes them a valuable tool for warehouse management system (WMS) barcode scanners, enabling efficient inventory tracking, product identification, and data collection. QR codes for inventory management can assist you in tracking a batch number or determining where a product was manufactured or imported from. QR codes are also secure because the data can be encrypted.
How To Use QR Code For Inventory Management?
Establishing a warehouse inventory scanning system with QR codes may initially require time and present some challenges. However, once the system is set up, and users become acquainted with the platform, the invested effort proves to be undeniably worthwhile.
Steps to set up the system:
- Use a QR code generator to create a unique QR code for each item in your inventory.
- Put a QR code on a sticker and stick it to each item in your inventory. This will make it easy to track each item.
- Store the QR code and important information about each item in your inventory software.
- To use the QR codes, just point your phone’s camera at them. This is much faster than looking up each item in your records.
THE PERKS OF USING A QR CODE FOR WAREHOUSING
Because QR Codes can hold more information than Barcodes, they were originally developed to modernize large inventory management systems. Today, they are used in many warehousing systems to manage large product volumes. Mainly, barcode scanners for warehouse management and the integration of barcodes in warehouse systems have become prevalent, especially for efficiently handling substantial product volumes.
The following are some of the advantages of using QR code inventory management software for warehouse operations over barcodes.
Readability
QR codes are 360 degrees scannable and you can scan them from any direction. Assume you’ve placed a slanted QR Code on your product. You can scan it and it is directed to the key information.
Storage Space
When you encode information in a QR code, it does not grow vertically. Data modules are used to store the information contained in QR Codes inventory management system. As a result, the QR Code becomes denser as more information is added.
As a result, QR Codes are small. It occupies less space and can easily place it on products of very small size.
Data Storage
QR codes for inventory tracking can store significantly more information and you can add up to 7,089 characters while one-dimensional barcodes can only store around 20-25 characters. Qr codes can store product information, website URLs, and plain text and maintain detailed information about every piece of Inventory.
Damage Resistant
An advantage of QR codes over barcodes is that a scanner can read partially damaged QR codes. Inventory management with QR codes can withstand up to 30% of damage. Miscounts caused by multiple scans of the same item are also excluded by QR codes.
THE BENEFITS OF USING CODE BASED OPERATIONS
Code-based operations are a powerful tool for warehouse management. They combine barcode scanners and warehouse management systems (WMS) to streamline processes, enhance visibility, and improve overall performance. This combination makes it easier to capture data, automate tasks, and make informed decisions, leading to a more efficient and proactive approach to warehouse management.
The use of QR code inventory management software in warehouse operations bring some of the following benefits:
Speed and Accuracy
Code-based operations allow for faster and more accurate data transfer which benefits the tracking of materials. You can track exactly the items location and can help speed up the processes. It saves your organisation time in responding to inquiries and changes. As it provides timely data information about products, it enhances warehouse productivity and maintains accurate inventory management.
Reduce Errors
Data capture that is quick and accurate reduces paperwork and the risk of errors. If an employee scans the particular code, the item gets entered. This capability eliminates errors when manually entering a damaged code.
Code-based scans are fast, reliable, and less time-consuming than manual data entry. When scanners read the codes, their graphics are quickly and accurately translated to a display without the errors often associated with manual data entry.
CHALLENGES IN THE ADOPTION OF QR CODES
It’s important to choose a system that works best for your organization. Not every company requires or desires to store so much data in a tracking code. They only require the SKU, price, and the ability to check it in or out of their system.
Many organisations already use barcode-based asset tracking and inventory management systems. For these organizations, removing labels and relabeling them with QR codes is not cost-effective and can be a time-consuming one. This could explain why QR codes haven’t taken off as quickly as expected. Implementing the QR codes scanners are much more expensive than barcode scanners.
The adoption of QR codes in barcode warehouse management systems is facing challenges related to cost and compatibility with existing systems. However, the potential benefits of QR codes are substantial, and organizations are exploring strategies to overcome these hurdles and harness the power of this technology.
According to Future Marketing Insights, the global QR code market was valued at $996.8 million in 2018 and is expected to increase annually by 8.7% between 2019 and 2027. The growing popularity of QR codes speaks volumes about the digital transformation that will occur shortly!

